 English
English 
 English
English 
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2026-01-09 Origin: Site











As a core metering device for bulk cargo trade, weighbridge development has aligned with industrial and logistics progress. Over a century, they evolved from traditional manual lever-based mechanical scales to intelligent IoT systems integrating sensors, IoT and big data, transforming from "weighing tools" to "intelligent metering terminals" and epitomizing industrial digital transformation. We trace this evolution to explore metering-driven industrial transformation logic.
Phase 1: The Mechanical Scale Era (Pre-mid-20th Century) – Industrial Enlightenment of the Lever Principle
Early weighbridges were dominated by mechanical scales based on the classic lever principle. Comprising a scale frame, lever mechanism, metering box and weights, they had a simple, robust structure with strong impact resistance. Using "weight increments + slider readings", they were widely used in mining, warehousing and agriculture. Power-independent, low-maintenance and usable on flat ground, they suited early industrialization's extensive production needs.
However, technical limitations brought obvious shortcomings: accuracy heavily relied on manual operation (minor slider deviations caused errors); limited weighing range; low efficiency requiring full-time operators; and no automatic data recording/tracing. Nevertheless, they laid the foundation for early industrial trade fairness and initiated the weighbridge industry.

Phase 2: The Electronic Scale Era (1980s – Early 21st Century) – Precision Revolution Driven by Sensor Technology
With industrial automation acceleration, mechanical scales' inefficiency and errors became a trade bottleneck. Electronic scales emerged in the 1980s, revolutionizing precision by upgrading from "mechanical force transmission" to "electrical signal conversion": strain gauge sensors convert weight to millivolt signals, processed by amplifiers and displayed digitally on electronic meters.
This phase brought three key leaps:
(1) Precision improved significantly (error <0.05%) for refined trade; (2) Efficiency boosted by eliminating manual weight/slider operations; (3) Initial functional expansion (data storage, printer connectivity for high-end models).
By 2015, electronic weighbridges accounted for over 95% of the market, replacing mechanical scales as mainstream.
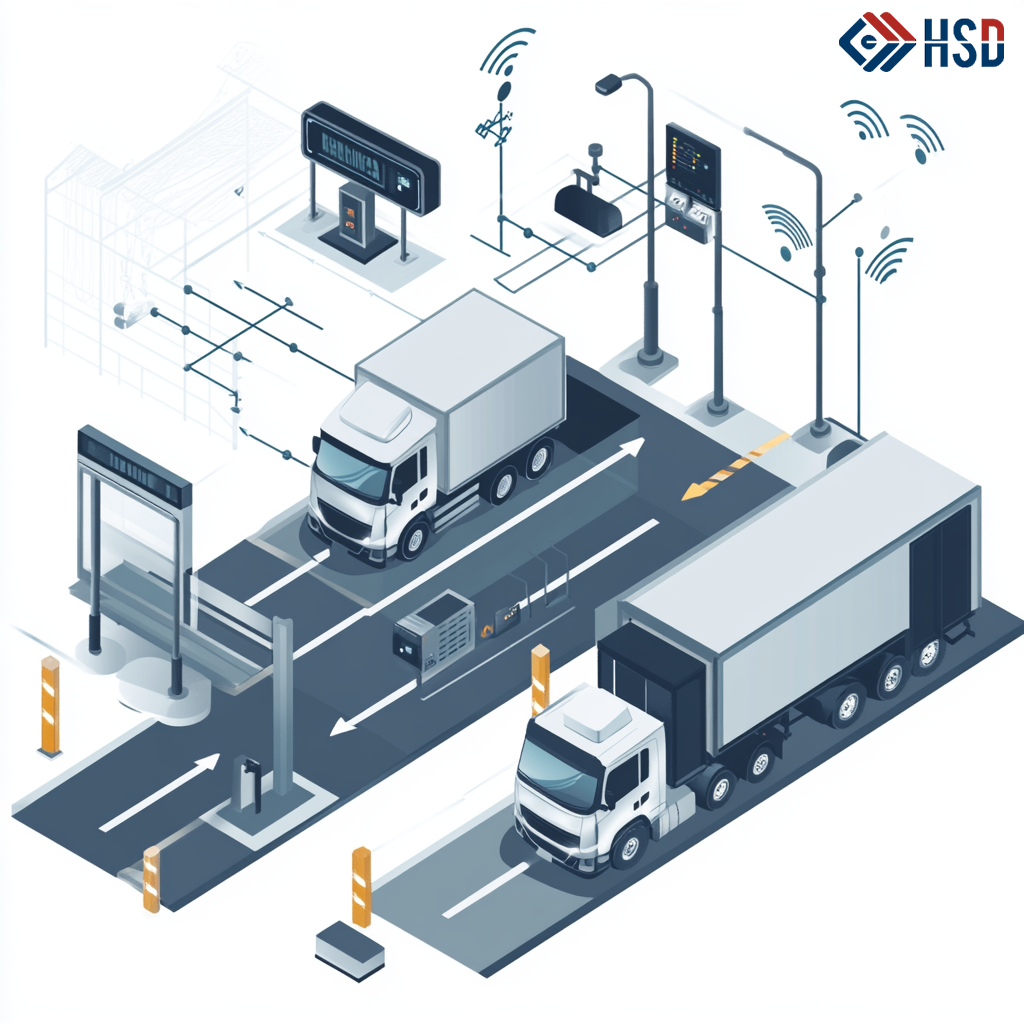
Phase 3: The Intelligent IoT Era (2010s – Present) – Efficiency Upgrade via Digital Integration
Entering the IoT era, the weighbridge industry has leaped from "electronic metering" to "intelligent IoT". Modern weighbridges are no longer isolated devices but end-to-end intelligent systems for "perception, transmission, analysis, and management", integrating sensor networks, wireless transmission, cloud computing, and edge computing. Their core features include three aspects:
Perception layer upgrade: Multi-type sensor arrays (e.g., strain gauges, fiber Bragg gratings) enable precise weight measurement and real-time environmental monitoring (temperature, humidity, gas), with automatic protection against corrosive gas damage. Edge computing optimization: Dedicated modules use improved Kalman filtering to suppress vibration, achieving 3,000 data fusions per second for stable dynamic weighing. Dual-mode transmission: LoRa and NB-IoT support 15km long-distance transmission (bit error rate <10⁻⁶), with encrypted key data for security.
More importantly, intelligent IoT weighbridges break traditional "data silos". Cloud-edge collaboration enables real-time data upload to cloud platforms, supporting remote monitoring, tracing, and fault diagnosis via mobile/PC. Digital twin-based 3D models realize visual equipment management and predictive maintenance. Industry data shows China has ~1.5 million weighbridges with only 35% intelligence rate; driven by smart logistics and Industry 4.0, this is expected to reach 70% in five years, making intelligent weighbridges a core trend.

Today, weighbridges have evolved from simple tools to intelligent terminals empowering logistics, mining and commercial concrete, supporting trade fairness, efficiency and management optimization. Looking ahead, 5G and AI integration will drive further evolution towards "unattended operation, automatic calibration and predictive maintenance", contributing to industrial digital transformation.
